CNN的训练及其架构
CNN的训练及其架构
CNN 的训练及其架构
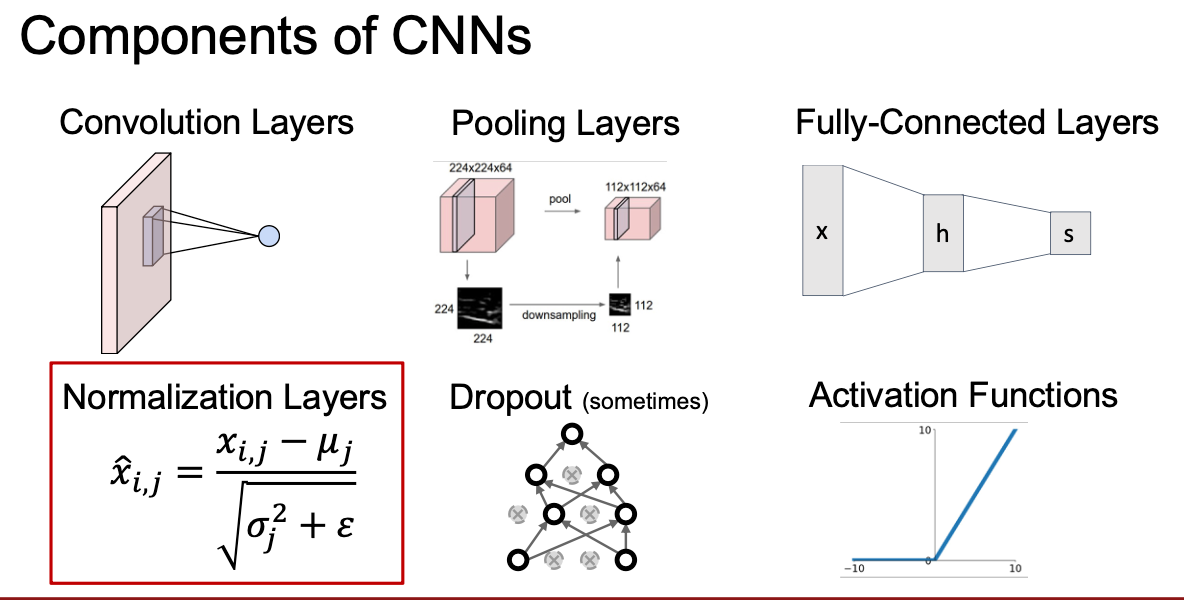
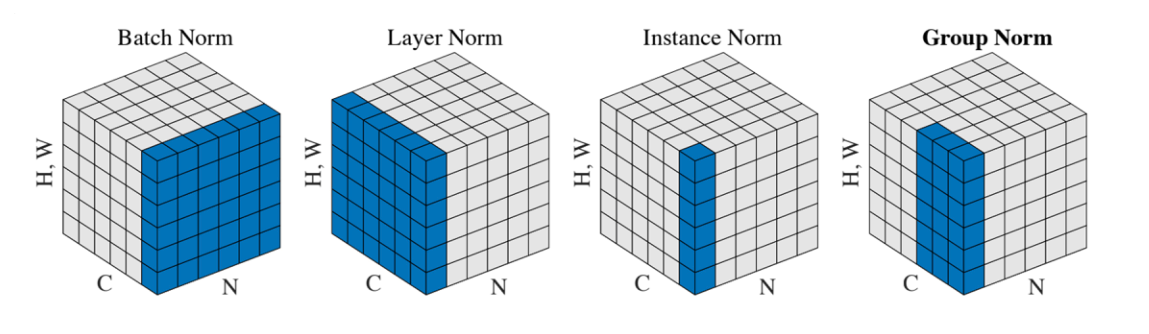
几种归一化方法
Layer Norm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
def layernorm_forward(x, gamma, beta, ln_param):
"""
Input:
- x: Data of shape (N, D)
- gamma: Scale parameter of shape (D,)
- beta: Shift paremeter of shape (D,)
- ln_param: Dictionary with the following keys:
- eps: Constant for numeric stability
Returns a tuple of:
- out: of shape (N, D)
- cache: A tuple of values needed in the backward pass
"""
out, cache = None, None
eps = ln_param.get("eps", 1e-5)
# per data-point mean/var across features
mu = np.mean(x, axis=1, keepdims=True) # (N,1)
var = np.var(x, axis=1, keepdims=True) # (N,1)
std = np.sqrt(var + eps) # (N,1)
inv_std = 1.0 / std # (N,1)
x_centered = x - mu # (N,D)
x_hat = x_centered * inv_std # (N,D)
out = gamma * x_hat + beta
cache = (x_hat, gamma, x_centered, inv_std, std, var, eps)
return out, cache
def layernorm_backward(dout, cache):
"""
Inputs:
- dout: Upstream derivatives, of shape (N, D)
- cache: Variable of intermediates from layernorm_forward.
Returns a tuple of:
- dx: Gradient with respect to inputs x, of shape (N, D)
- dgamma: Gradient with respect to scale parameter gamma, of shape (D,)
- dbeta: Gradient with respect to shift parameter beta, of shape (D,)
"""
x_hat, gamma, x_centered, inv_std, std, var, eps=cache
N, D = dout.shape
dbeta = np.sum(dout, axis=0) # (D,)
dgamma = np.sum(dout * x_hat, axis=0) # (D,)
dxhat = dout * gamma # (N,D)
sum_dxhat = np.sum(dxhat, axis=1, keepdims=True) # (N,1)
sum_dxhat_xhat = np.sum(dxhat * x_hat, axis=1, keepdims=True) # (N,1)
dx = (1.0 / D) * inv_std * (D * dxhat - sum_dxhat - x_hat * sum_dxhat_xhat)
return dx, dgamma, dbeta
Batch Norm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
def batchnorm_forward(x, gamma, beta, bn_param):
"""
Input:
- x: Data of shape (N, D)
- gamma: Scale parameter of shape (D,)
- beta: Shift paremeter of shape (D,)
- bn_param: Dictionary with the following keys:
- mode: 'train' or 'test'; required
- eps: Constant for numeric stability
- momentum: Constant for running mean / variance.
- running_mean: Array of shape (D,) giving running mean of features
- running_var Array of shape (D,) giving running variance of features
Returns a tuple of:
- out: of shape (N, D)
- cache: A tuple of values needed in the backward pass
"""
mode = bn_param["mode"]
eps = bn_param.get("eps", 1e-5)
momentum = bn_param.get("momentum", 0.9)
N, D = x.shape
running_mean = bn_param.get("running_mean", np.zeros(D, dtype=x.dtype))
running_var = bn_param.get("running_var", np.zeros(D, dtype=x.dtype))
out, cache = None, None
if mode == "train":
sample_mean = np.mean(x, axis=0)
sample_var = np.var(x, axis=0)
x_centered = x - sample_mean # (N,D)
std = np.sqrt(sample_var + eps) # (D,)
inv_std = 1.0 / std # (D,)
x_hat = x_centered * inv_std #(N,)
out = gamma * x_hat + beta
running_mean = momentum * running_mean + (1 - momentum) * sample_mean
running_var = momentum * running_var + (1 - momentum) * sample_var
cache = (x_hat, gamma, x_centered, inv_std, std, sample_var, eps)
elif mode == "test":
x_hat = (x - running_mean) / np.sqrt(running_var + eps)
out = gamma * x_hat + beta
cache = None
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid forward batchnorm mode "%s"' % mode)
# Store the updated running means back into bn_param
bn_param["running_mean"] = running_mean
bn_param["running_var"] = running_var
return out, cache
Dropout(以一定的概率丢掉一些神经元来防止过拟合)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
def dropout_forward(x, dropout_param):
"""
Performs the forward pass for (inverted) dropout.
Inputs:
- x: Input data, of any shape
- dropout_param: A dictionary with the following keys:
- p: Dropout parameter. We keep each neuron output with probability p.
- mode: 'test' or 'train'. If the mode is train, then perform dropout;
if the mode is test, then just return the input.
- seed: Seed for the random number generator. Passing seed makes this
function deterministic, which is needed for gradient checking but not
in real networks.
Outputs:
- out: Array of the same shape as x.
- cache: tuple (dropout_param, mask). In training mode, mask is the dropout
mask that was used to multiply the input; in test mode, mask is None.
NOTE: Please implement **inverted** dropout, not the vanilla version of dropout.
See http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-2/#reg for more details.
NOTE 2: Keep in mind that p is the probability of **keep** a neuron
output; this might be contrary to some sources, where it is referred to
as the probability of dropping a neuron output.
"""
p, mode = dropout_param["p"], dropout_param["mode"]
if "seed" in dropout_param:
np.random.seed(dropout_param["seed"])
mask = None
out = None
if mode == "train":
mask = (np.random.rand(*x.shape) < p) / p
out = x * mask
elif mode == "test":
out=x
cache = (dropout_param, mask)
out = out.astype(x.dtype, copy=False)
return out, cache
def dropout_backward(dout, cache):
"""
Perform the backward pass for (inverted) dropout.
Inputs:
- dout: Upstream derivatives, of any shape
- cache: (dropout_param, mask) from dropout_forward.
"""
dropout_param, mask = cache
mode = dropout_param["mode"]
dx = None
if mode == "train":
dx=dout * mask
elif mode == "test":
dx = dout
return dx
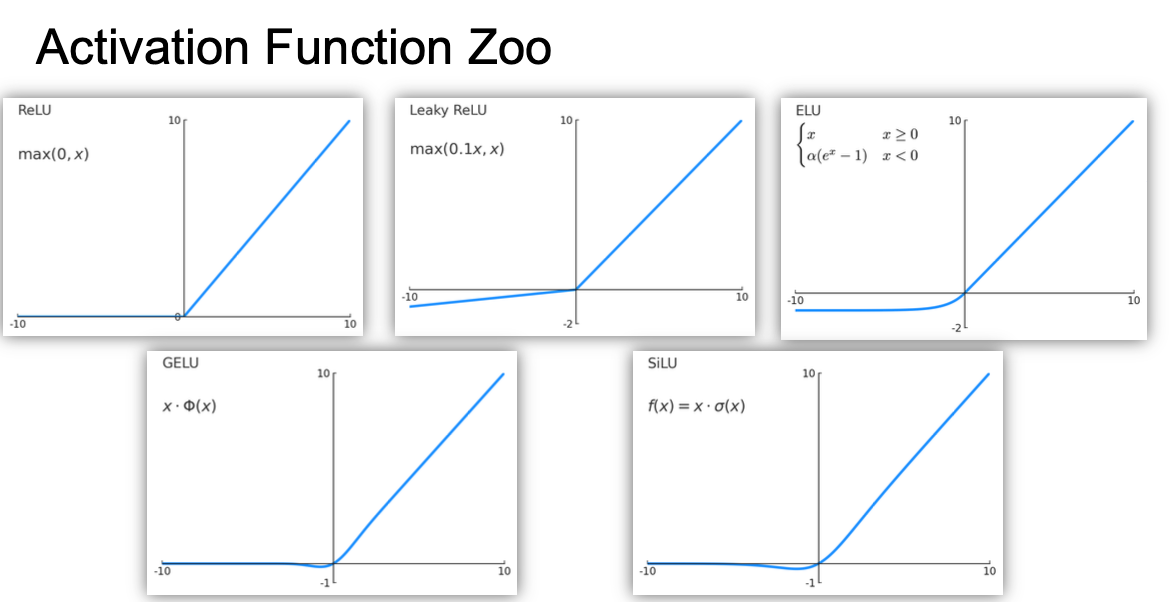
激活函数
Sigmoid : $\sigma(x)=1/(1+ e^{-x})$
Problem:
- 多层sigmoids叠加的时候梯度会越来越小从而发生梯度消失
- 当$x$ 为很大的正数或负数的时候,会杀死梯度导致梯度消失
Relu: $F(x)=\max(0,x)$
优点:
- 梯度计算方便
- 收敛速度快(比sigmoid快6倍)
Problem:
- 对于小于0的数会被直接省略导致没有以0为中心的输出
Gelu:
- 比Relu的计算成本高但是就算是大的负数也可以有$\rightarrow0$的梯度
基本结构
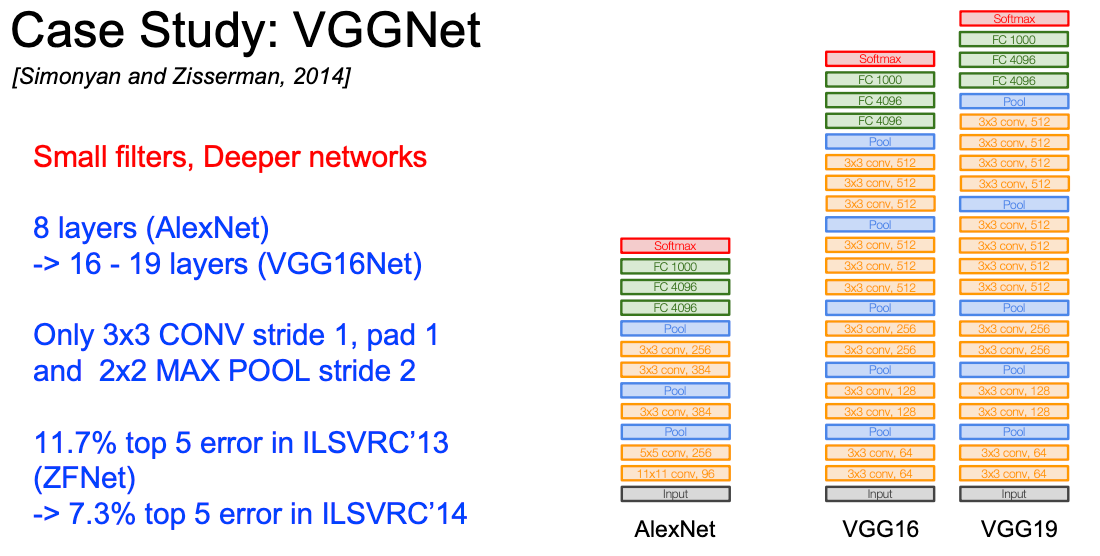
VGGNet系列
为什么用$3\times 3$ 的小卷积核?
Stack of three 3x3 conv (stride 1) layers has same effective receptive field as one 7x7 conv layer
But deeper, more non-linearities
And fewer parameters: $3*(3^2C^2)$ vs.$7^{2} C^2$for C channels per layer
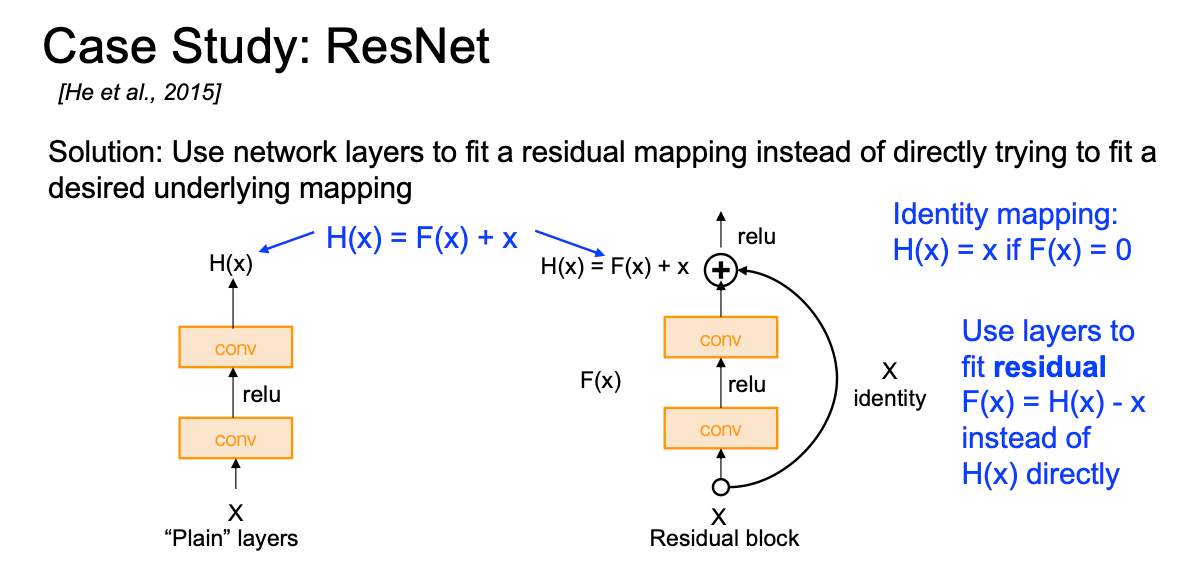
ResNet: 深度改革
研究发现:越深的模型表现在训练和测试误差比小模型更差而且不少因为过拟合导致的, 因为模型越深优化难度越大
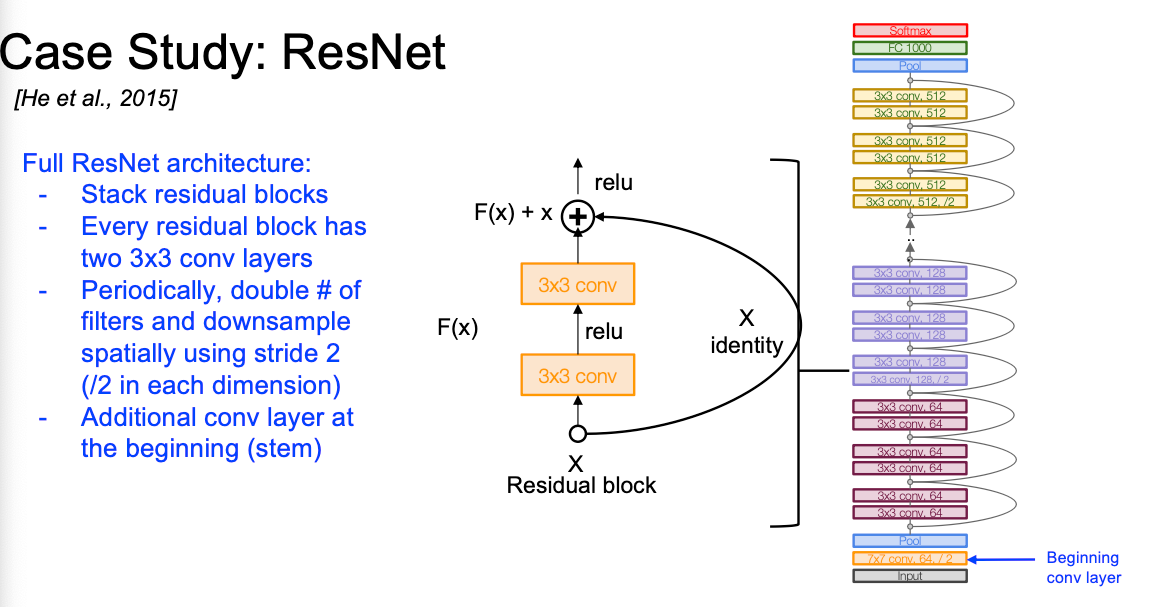
具体架构如下,将残差块迭起来
权重初始化
MSRA 初始化
不硬性要求而是软性要求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
dims=[4096]*7
hs=[]
x=np.random.randn(16,dims[0])
for Din,Dout in zip(dims[:-1],dims[1:]):
w = np.random.randn(Din,Dout)* np.sqrt(2/Din)
x = np.maximum(0,x.dot(W))
hs.append(x)
数据预处理:归一化/数据增强
Subtract per-channel mean and Divide by per-channel std (almost all modern models)
1
norm_pixel[i,j,c]=(pixel[i,j,c]-np.mean(pixel[:,:,c])) / np.std(pixel[:,:,c])
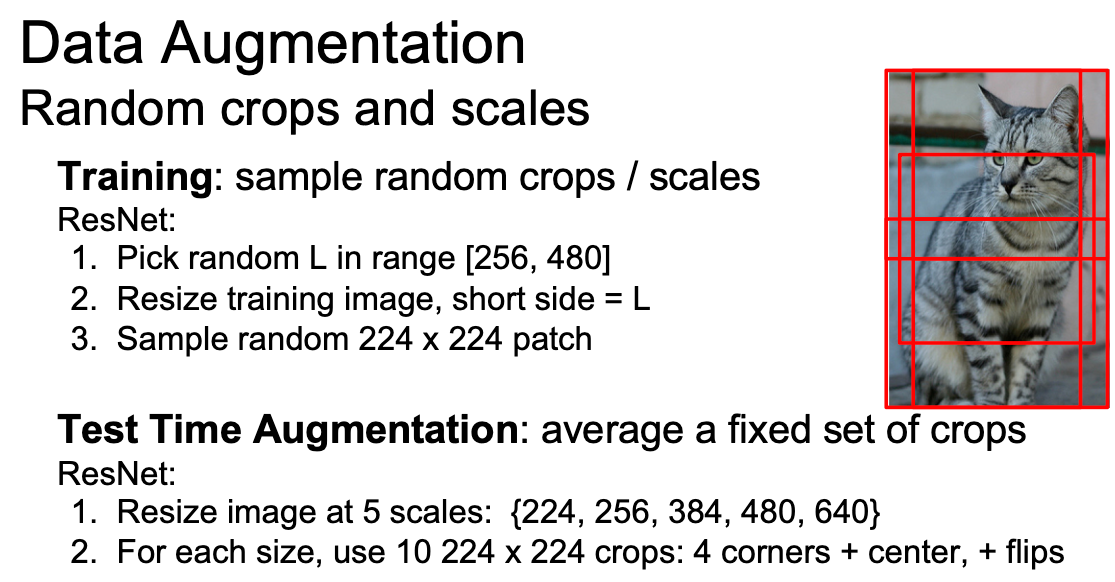
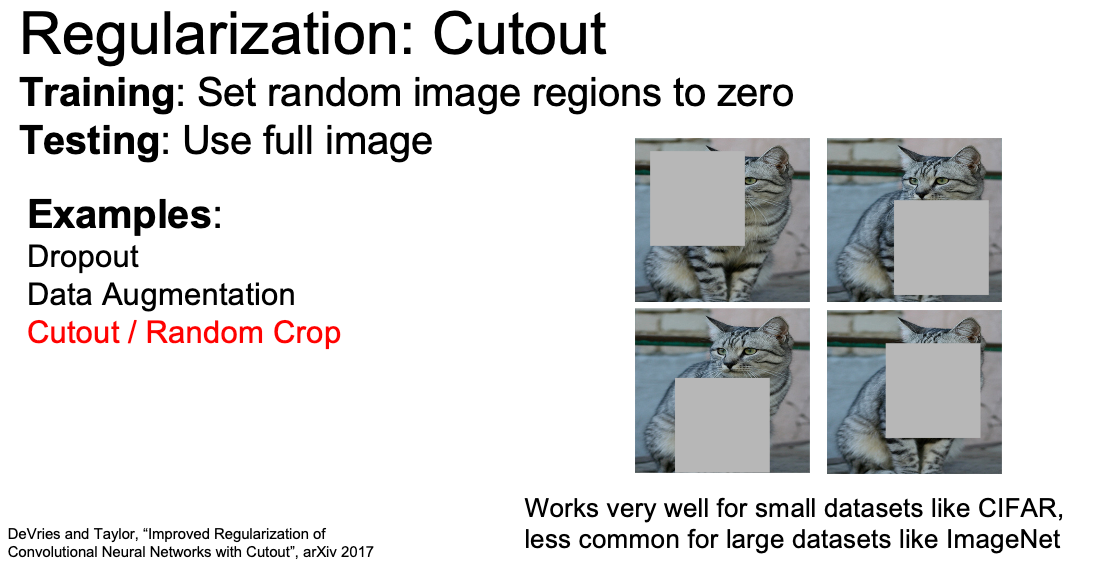
数据增强
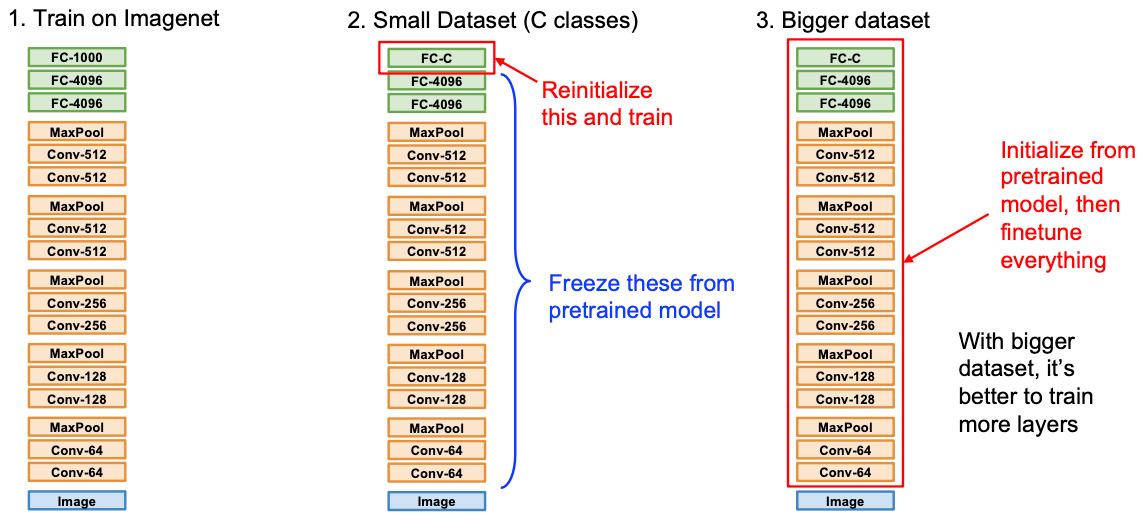
微调(训练数据少的时候)
| 相似数据集 | Different Dataset | |
|---|---|---|
| 数据量少 | 在最后一层用一个线性分类器或者接一个小模型只训这个小模型 | 尝试另一个model或者收集更多的数据 |
| 数据量多 | 微调所有层 | 微调所有层或者从0开始训 |
超参数的调整
第一步: 调整学习率,然后看损失曲线,可以用grid search 或者给定区间的随机搜索
Good learning rates to try: 1e-1, 1e-2, 1e-3, 1e-4, 1e-5
第二步:看准确度曲线和损失曲线
- 准确度稳定上升证明训时间不够
- 训练集准确度$\Uparrow$ 验证集准确度下降
- 过拟合,考虑加正则项惩罚模型规模或者加多点数据量
- 训练集和验证集的准确度之间没有gap
- 欠拟合:训久一点,可以考虑用大一点的模型
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.