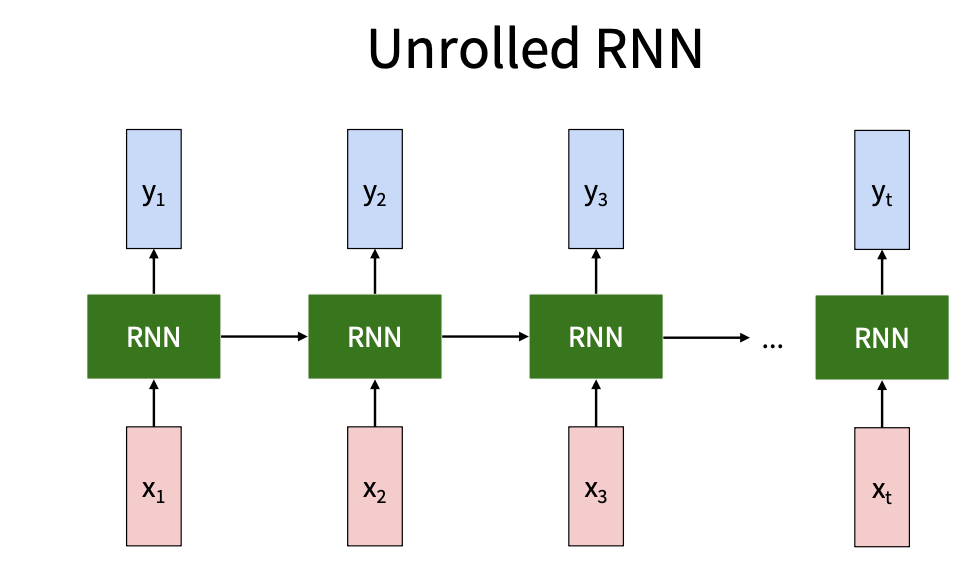
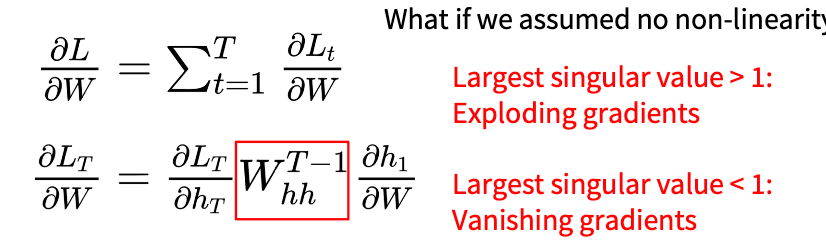RNN
RNN
RNN(循环神经网络)
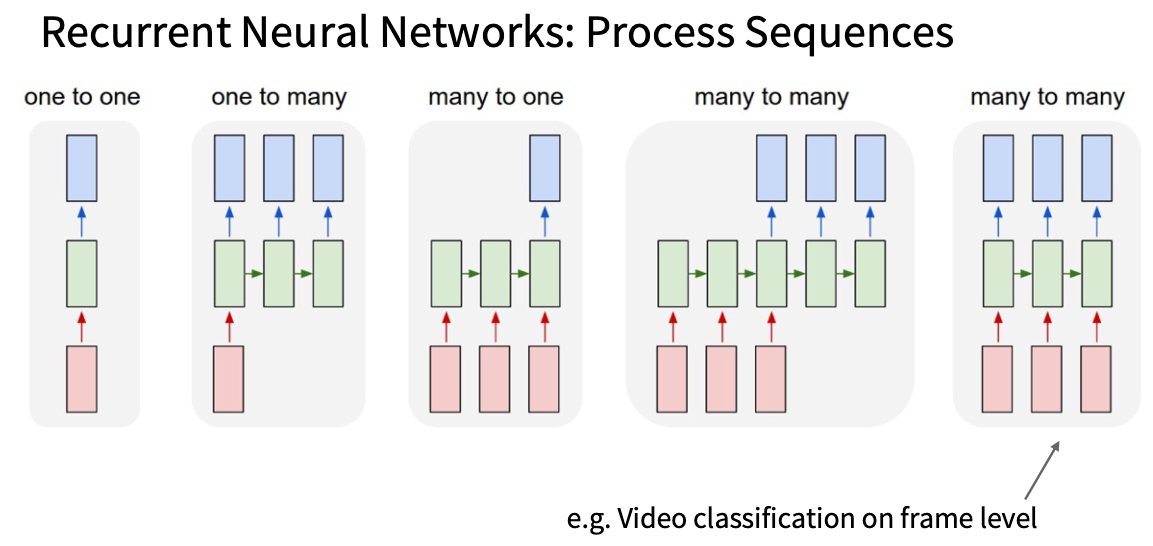
用来处理序列化输入,分为以下几种
本质: 通过一些internal state把序列连接起来
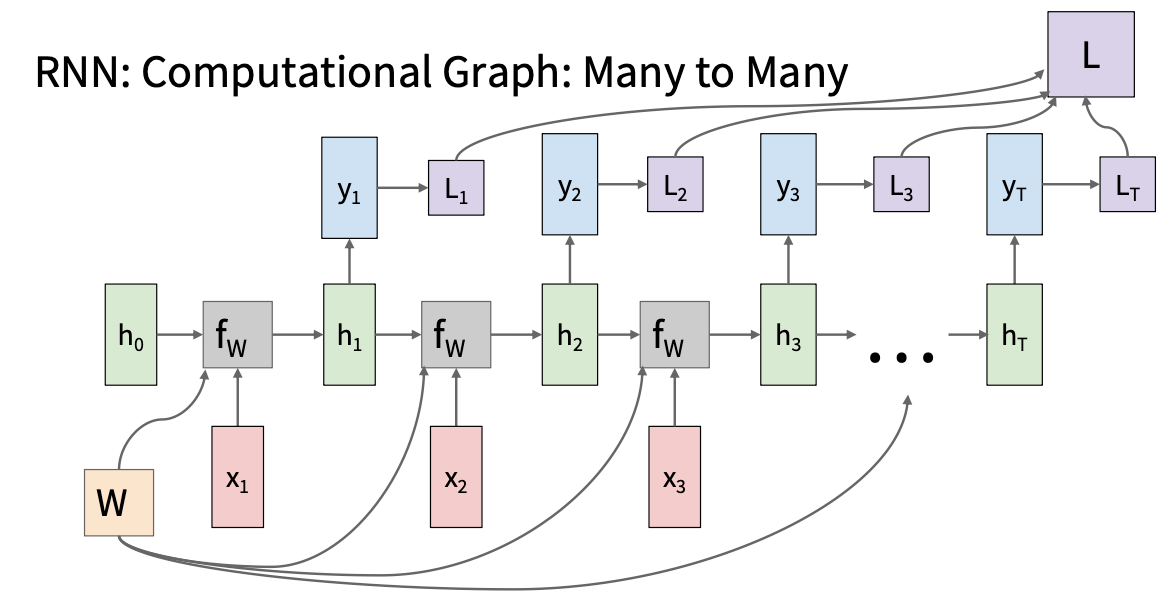
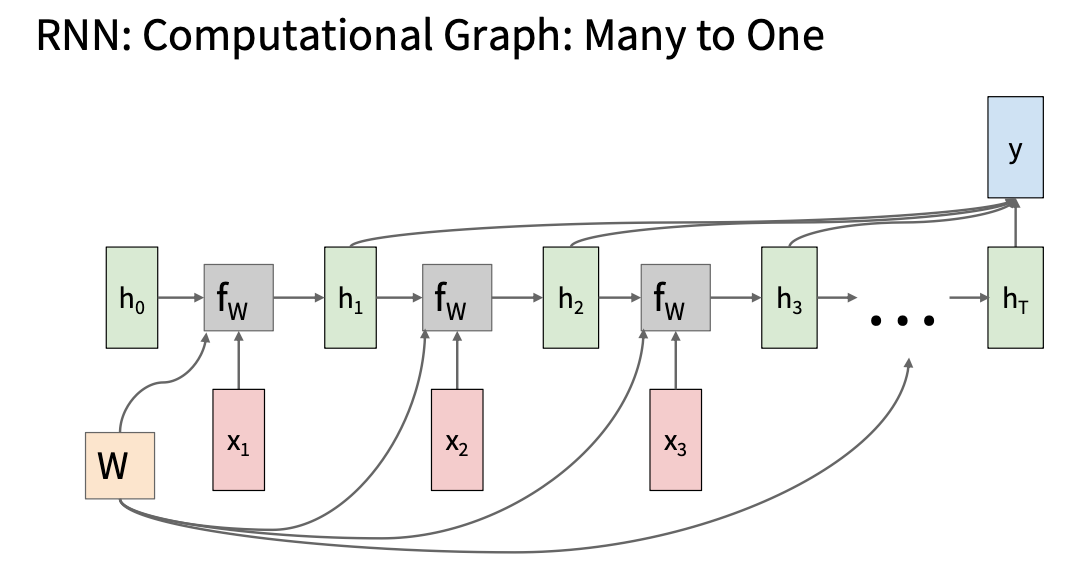
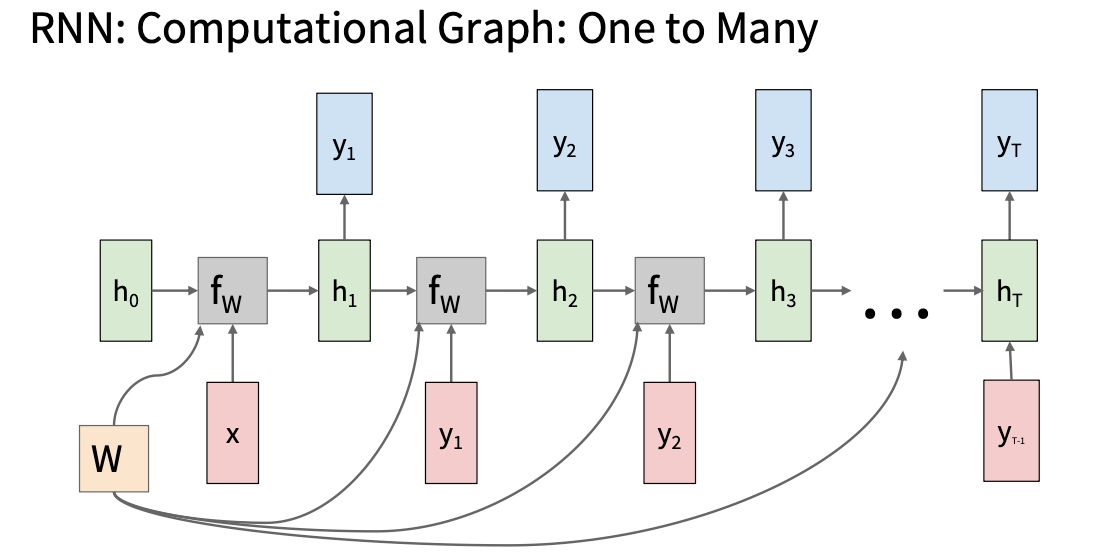
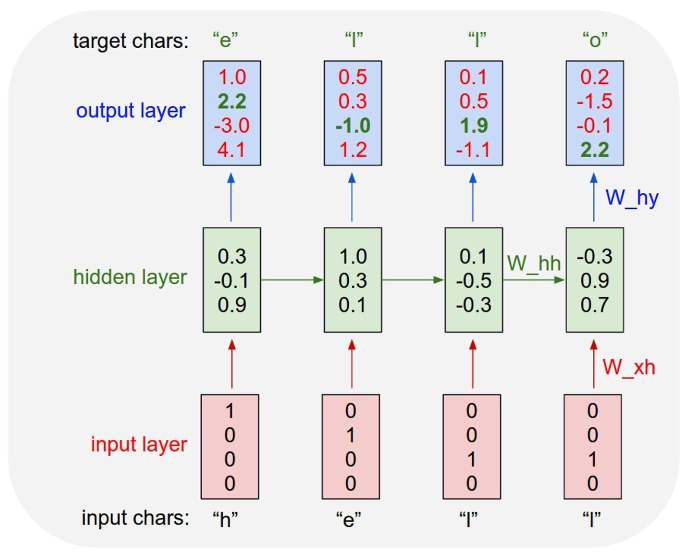
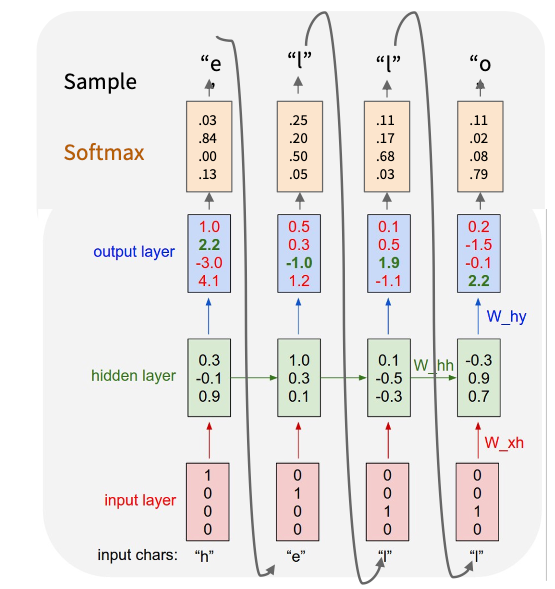
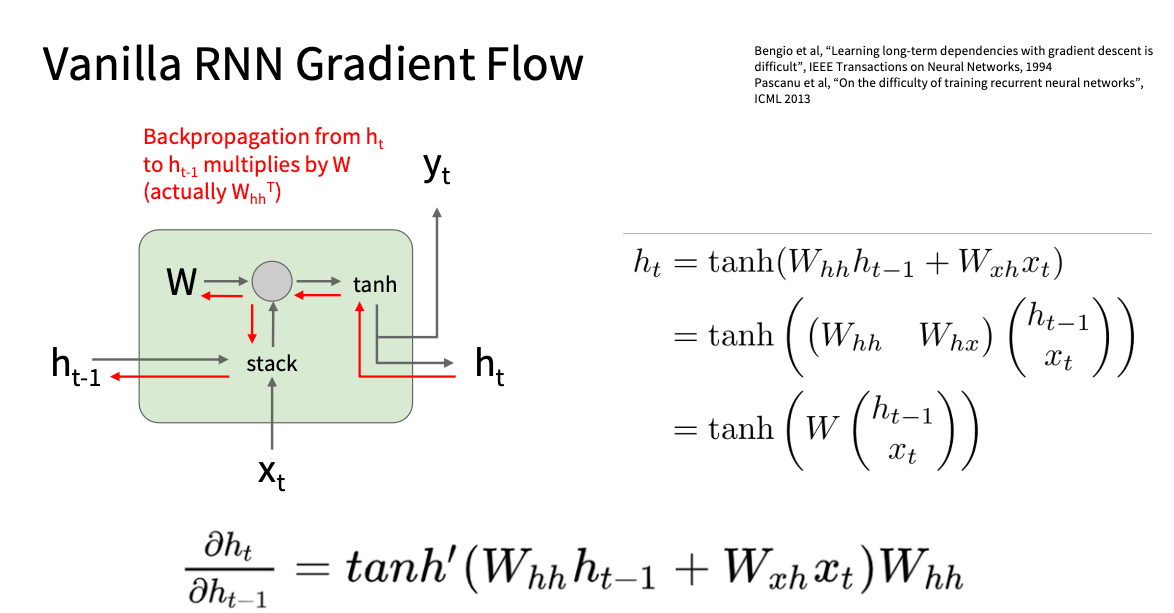
 \(h_t=f_w(h_{t-1},x_t)=\tanh(W_{hh}h_{t-1}+W_{xh}x_t)\\ y_t=f_{W_{hy}}(h_t)=W_{hy}h_t\) 注意: 所有的时间步共享一个权重矩阵
\(h_t=f_w(h_{t-1},x_t)=\tanh(W_{hh}h_{t-1}+W_{xh}x_t)\\ y_t=f_{W_{hy}}(h_t)=W_{hy}h_t\) 注意: 所有的时间步共享一个权重矩阵
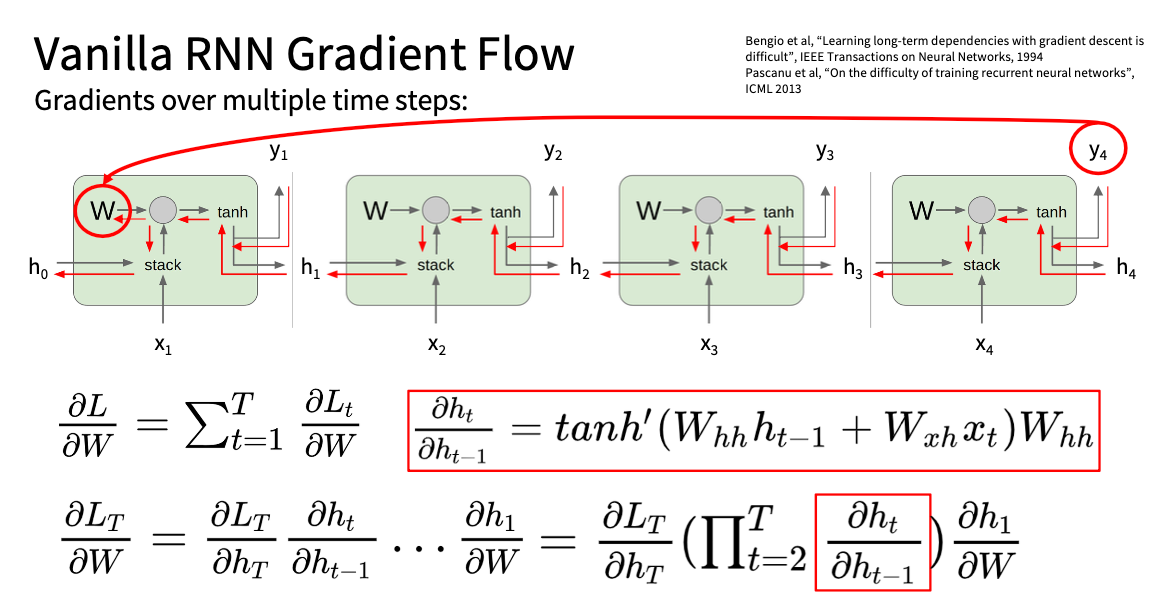
反向传播的时候采取截断的反向传播法
Carry hidden states forward in time forever,
but only backpropagate for some smaller number of steps
训练阶段(监督学习)
测试阶段
优缺点总结
优点:
- 没有上下文长度限制可以处理任意长度的输入
- 时刻$t$的计算可以用到过去的信息
- 由于共享模型权重,所以模型大小不会随着输入长度变长而变大且输入的处理是对称的
缺点:
- 时间久速度慢
- 而且在实际应用中information的利用对过去时间步长度都有要求.
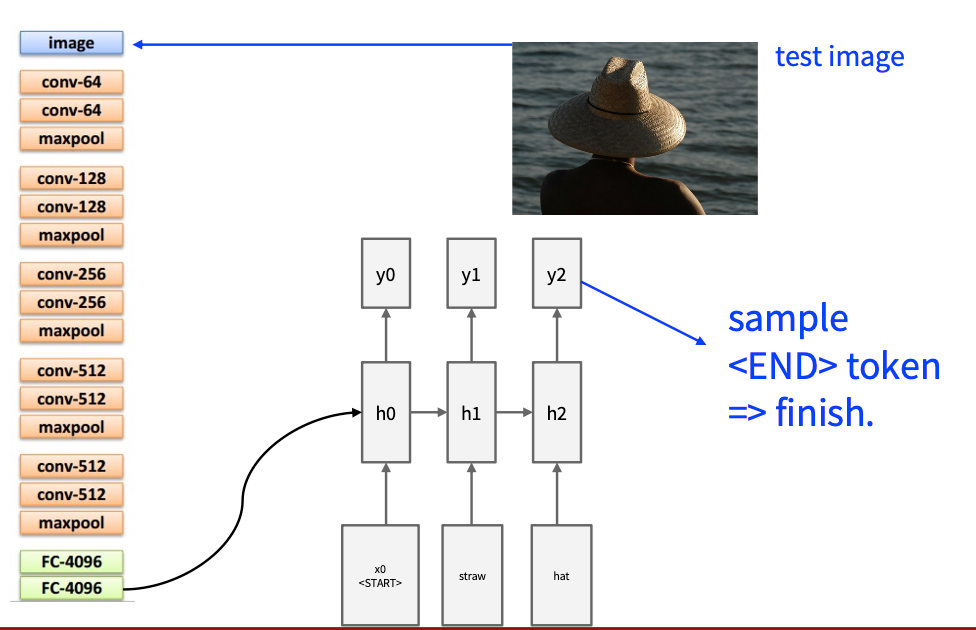
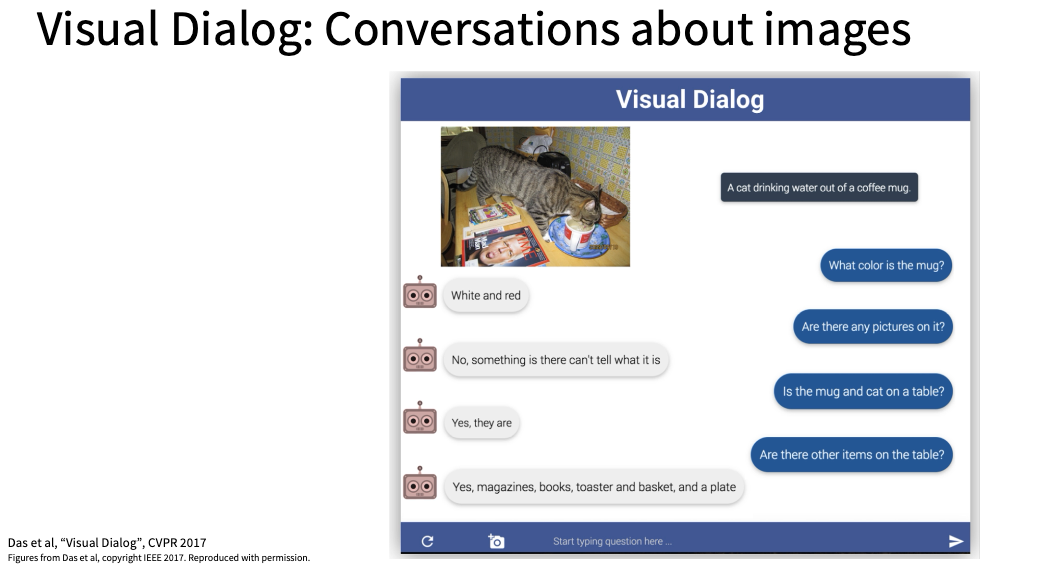
应用方面
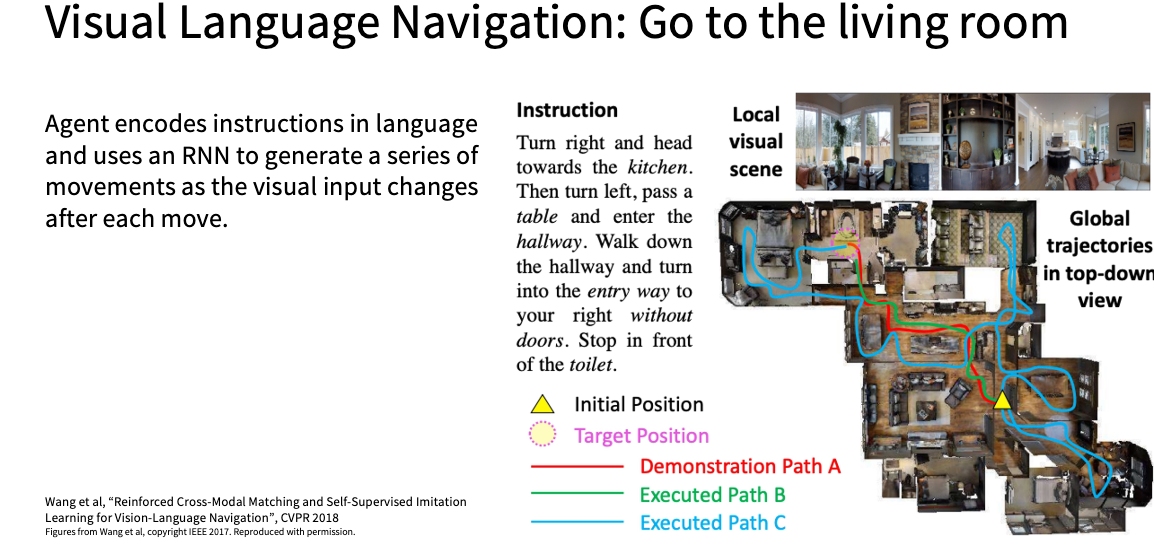
Image Captioning
梯度传播
加入我们忽略没有非线性变换则会出现如下问题
- 最大奇异值>1: 采取梯度裁剪,梯度大于一个值就进行缩放
1
2
3
grad_norm= np.sum(grad * grad)
if grad_norm > threshold:
grad *=(threshold/ grad_norm)
- 最大奇异值<1:改变RNN 架构
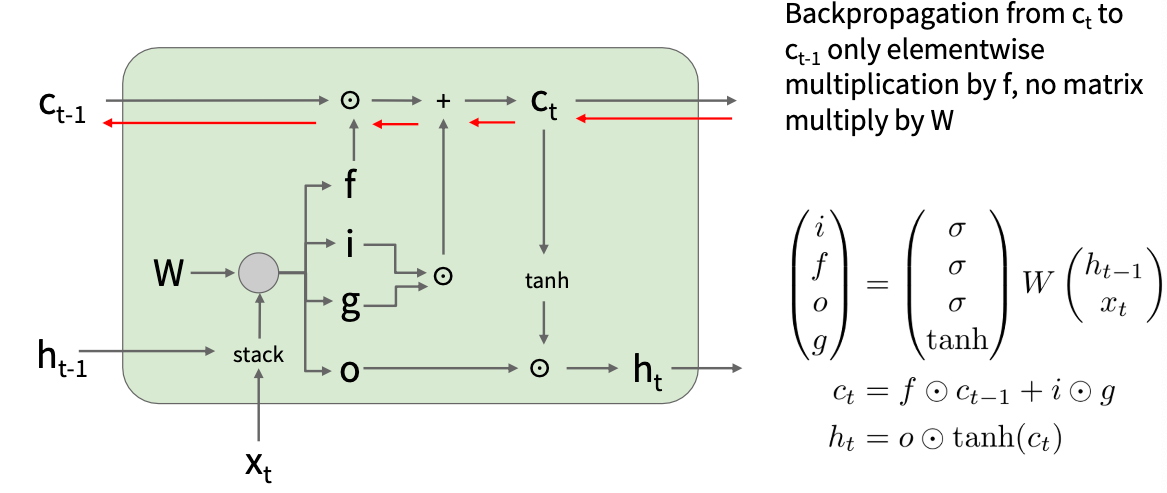
LSTM(解决梯度消失)
- i(输入门):决定是否写入shell
- f(遗忘门):决定是否erase shell
- o(输出门):How much to reveal shell
- g():How much to write to cell
现代RNN(State Space Model)
- 无限上下文长度
- 计算量随着模型长度线性增长
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.