计算机视觉的主要任务和进展
计算机视觉任务、可视化和理解
Semantic Segmentation
训练集: 给每个像素点 打上语义类别标签
测试 : 给图片的每个像素点分类
思路一: Sliding Window ,上下文提取特征
Learning Hierarchical Features for Scene Labeling(TPAMI 2013)
Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Scene Labeling(ICML 2014)
问题:效率很低,没有利用重叠的patchs的共享features.
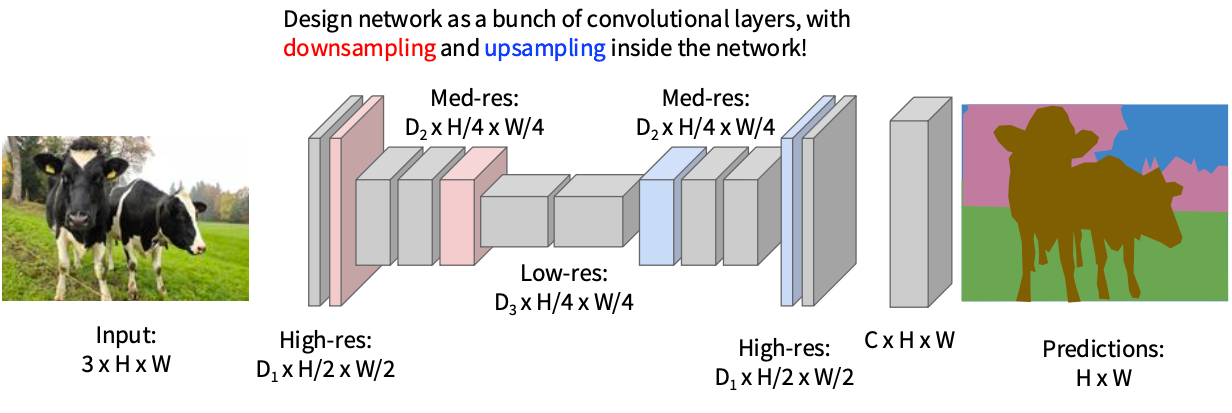
思路二:全卷积
idea1: 提取上下文空间特征,不下采样从而保证输出和输入的shape一致$\Rightarrow$ 太贵了
Idea2:先下采样然后再上采样来keep shape
Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation(CVPR 2015)
Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation(ICCV 2015)
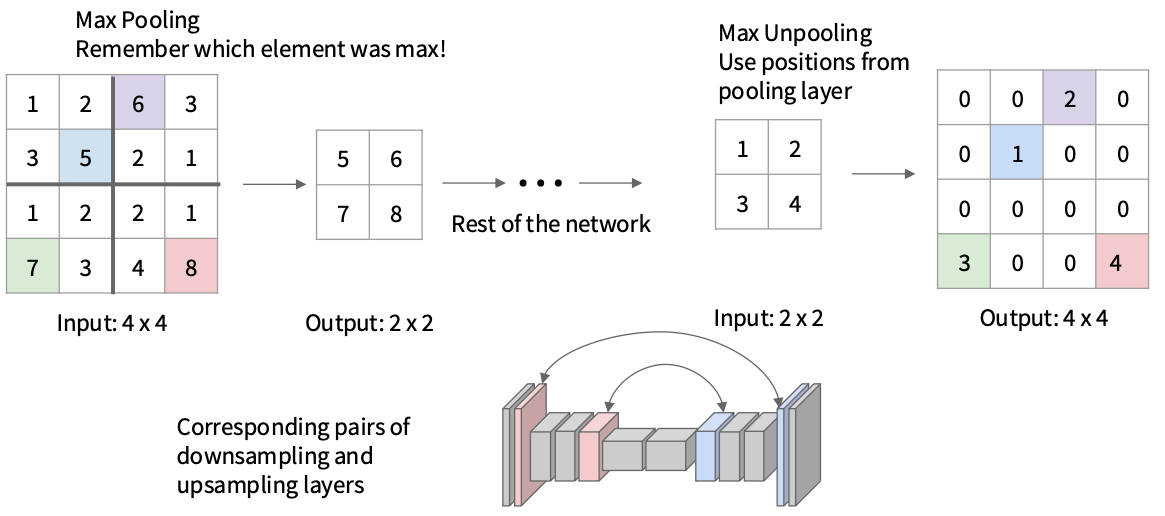
下采样 : 先Pooling 再 Stride Convolution
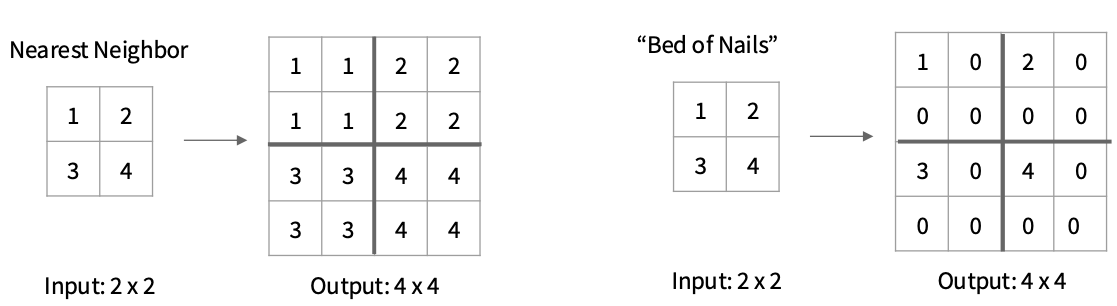
上采样 : Unpooling
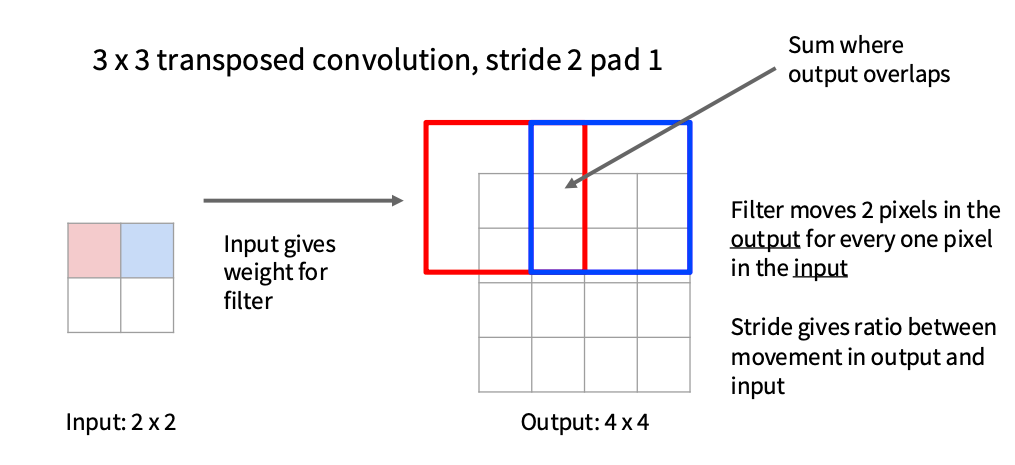
可学习的版本: 反卷积(Transpose Convolution)
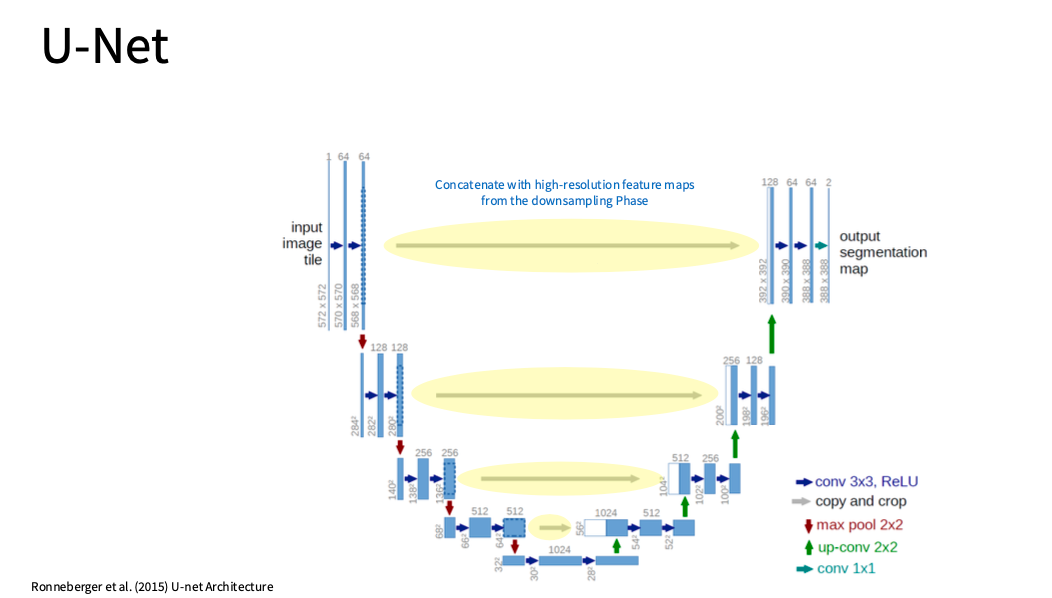
思路三: U-Net
$\color{red} 别关心实例,只关注像素 $
- 先downsampling 再upsampling
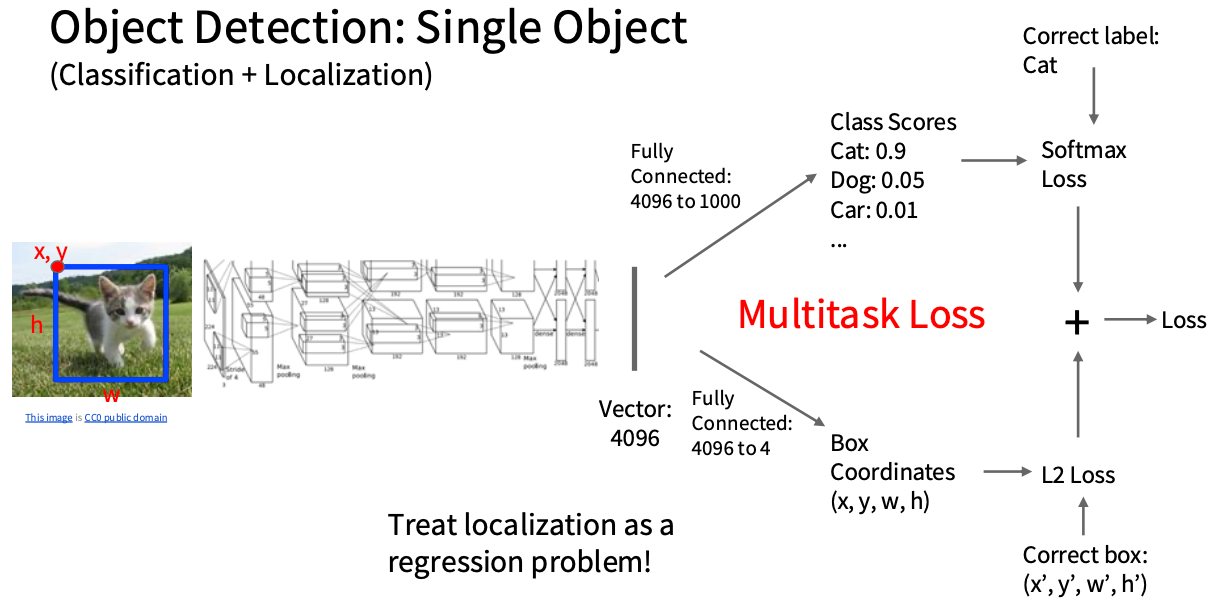
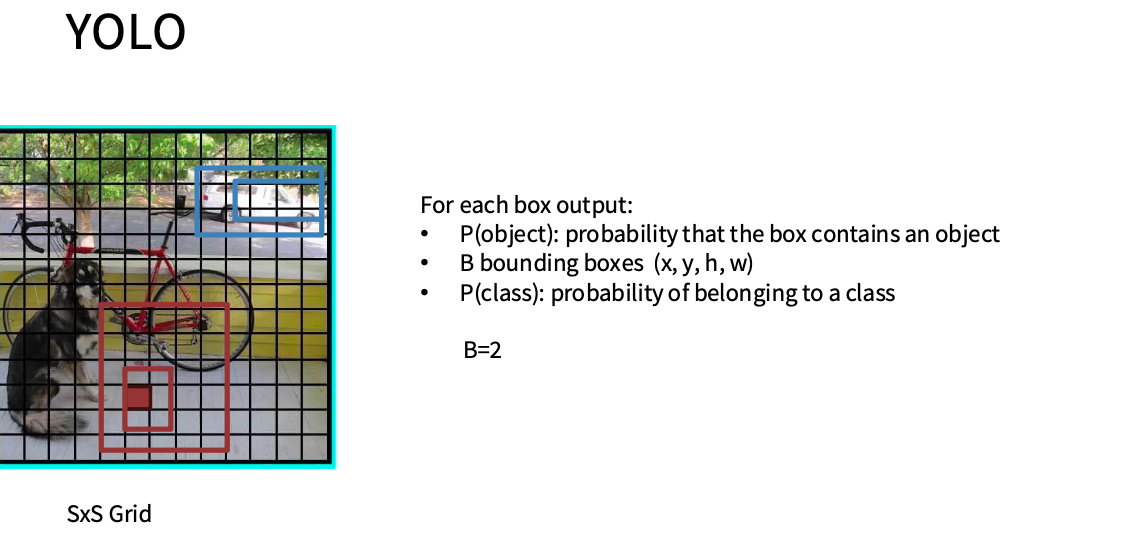
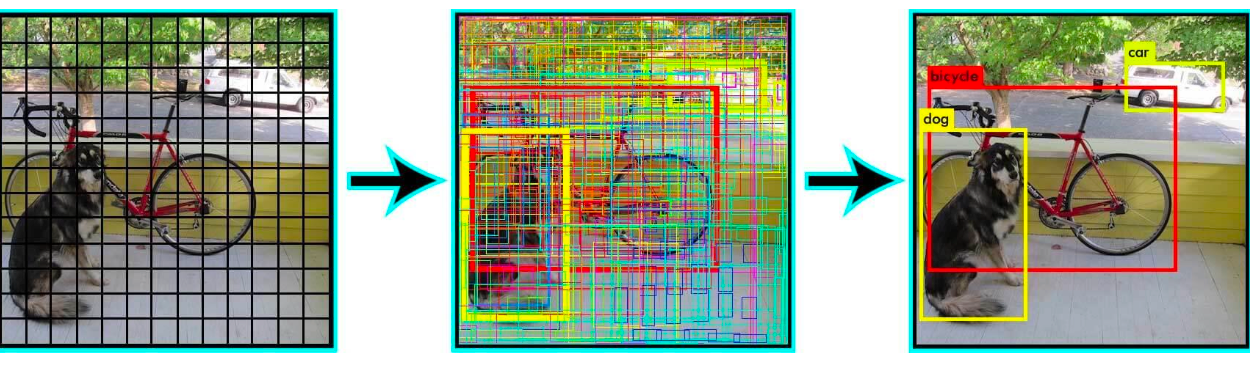
物体检测=Classification + Localization
但是对于多物体检测, Each image needs a different number of outputs!
思路一: 将图片分成多个patch然后分别进行单物体检测
Problem: Need to apply CNN to huge number
of locations, scales, and aspect ratios, very
computationally expensive!
思路二: Region Proposals: Selective Search
● Find “blobby” image regions that are likely to contain objects
● Relatively fast to run; e.g. Selective Search gives 2000 region
proposals in a few seconds on CPU
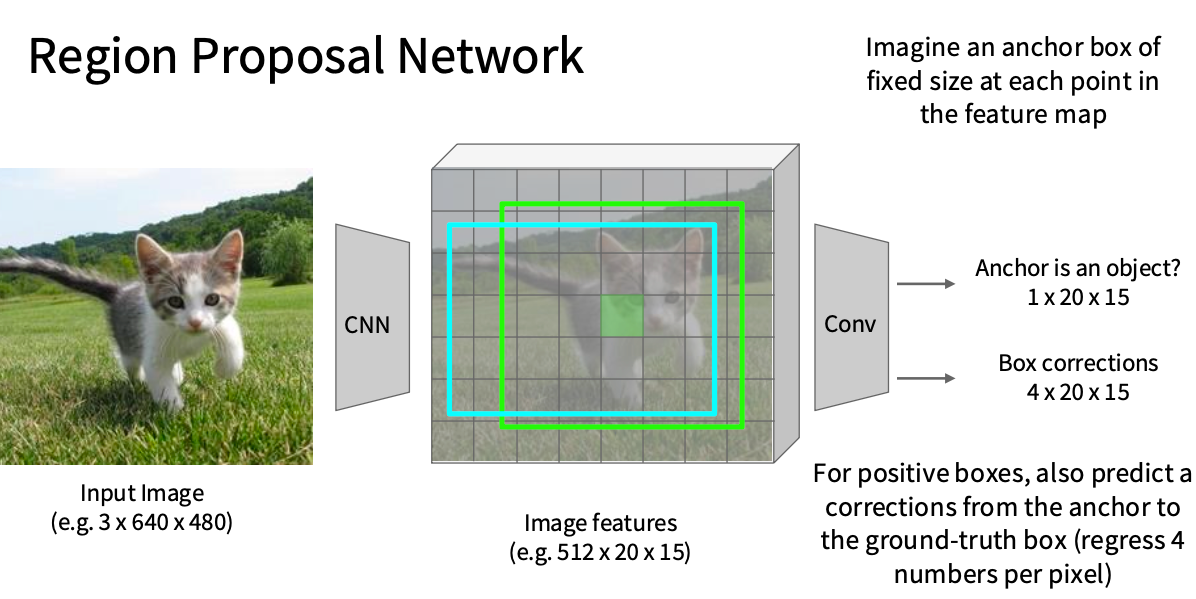
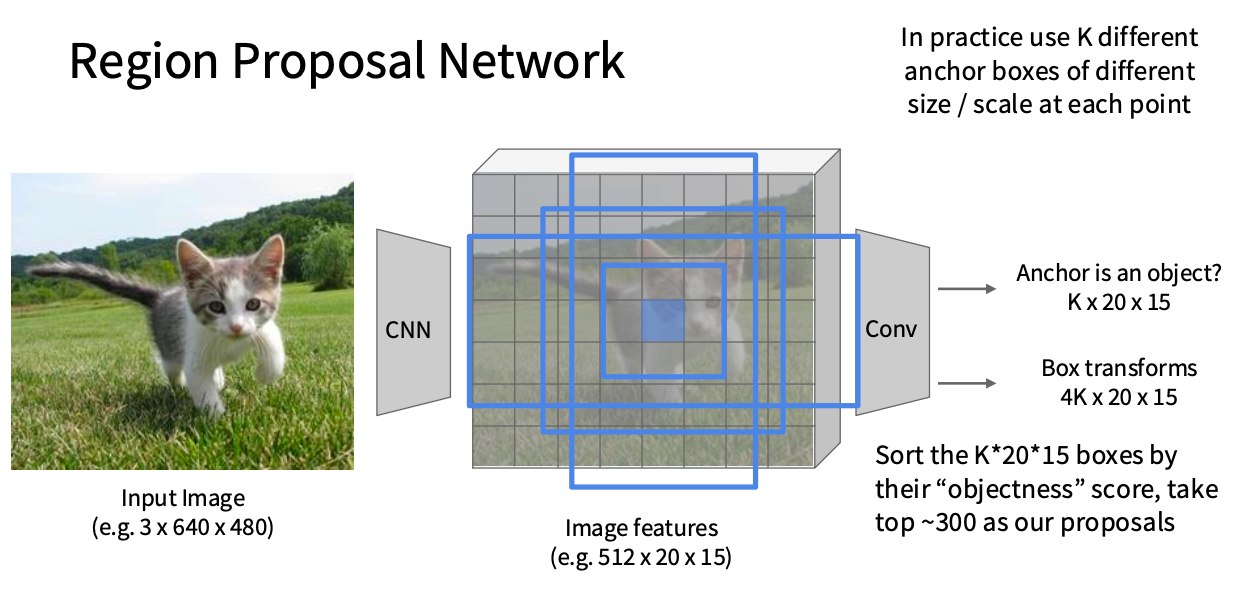
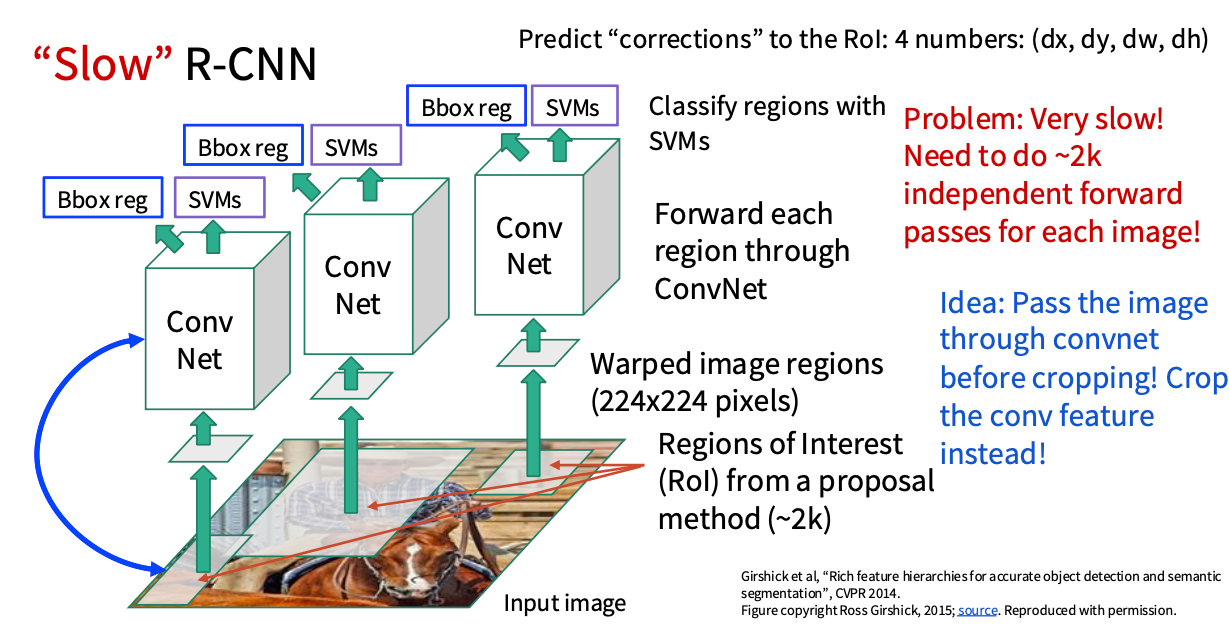
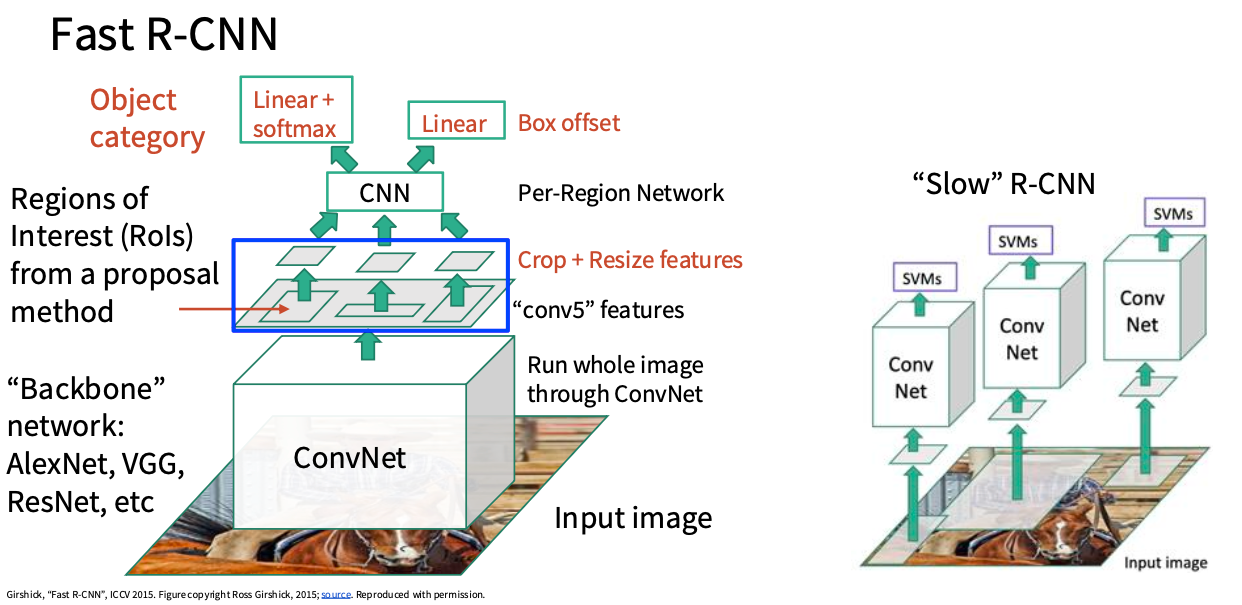
思路三: R-CNN
Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation(CVPR 2014)